Cos 2
Cos y = x.

Cos 2. The R method is most often used to find the extrema (maximum and minimum) of combinations of trigonometric functions. G(x) = 6 cos(x), −π/2, π/2 gave =. Names of standardized tests are owned by the trademark holders and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors LLC.
Using this technique the number i can be written. 4.9/5.0 Satisfaction Rating over the last 100,000 sessions. This means that the value of cos x becomes 0 or the value of cos x vanishes when x happens to be the odd multiple of π/2.
This estimate is accurate to four decimal places. This Demonstration compares the curves and. Let us find the general solutions of 2sin x = -1.
To do this I usually think of the geometric representation of the number in the complex plane. 0 ≤ θ ≤ π. Cos (θ + 2π) = cos θ.
X = ±π/3 +2kπ or x = ±π/2 +2kπ, where k is any integer. You where given cos x= + 2/3, so the x value is either between ) to pi/2 or 2pi/2 to 2pi, WHICH is what we want, but then the sin x value is NEGATIVE in this range. These trigonometry functions have extraordinary noteworthiness in Engineering.
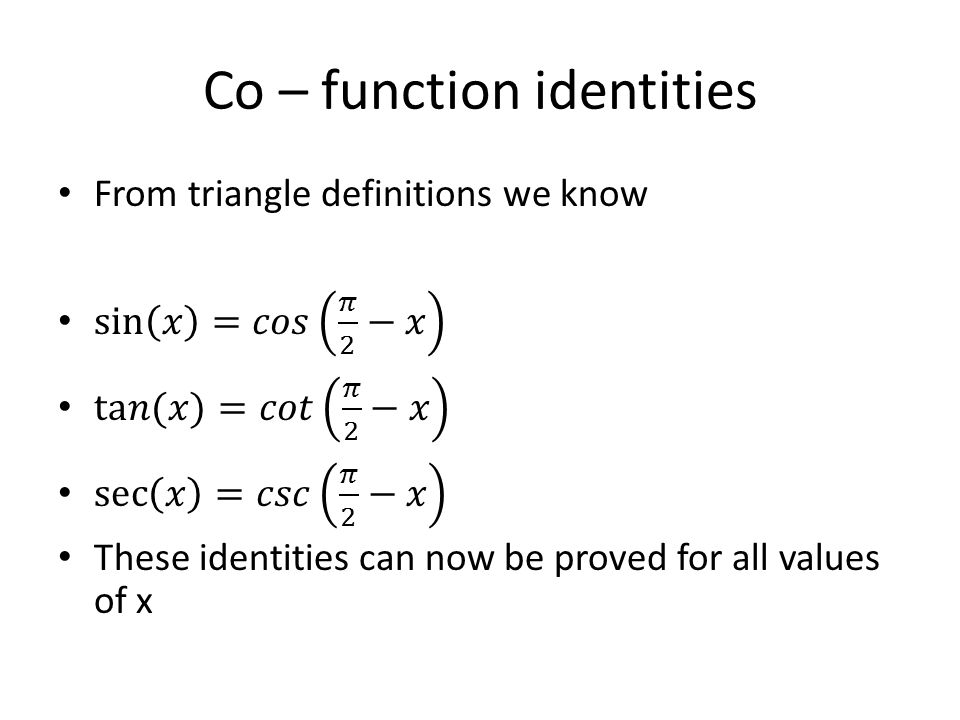
Because cos θ = b c = sin (π 2 − θ), cos θ = b c = sin (π 2 − θ), we have sin − 1 (cos θ) = π 2 − θ sin − 1 (cos θ) = π 2 − θ if 0 ≤ θ ≤ π. Trigonometric co-function identities are relationships between the basic trigonometric functions (sine and cosine) based on complementary angles.They also show that the graphs of sine and cosine are identical, but shifted by a constant of π 2 \frac{\pi}{2} 2 π. The six trigonometric functions can be defined as coordinate values of points on the Euclidean plane that are related to the unit circle, which is the circle of radius one centered at the origin O of this coordinate system.
The trigonometric R method is a method of rewriting a weighted sum of sines and cosines as a single instance of sine (or cosine). Cos y = x. OR (my method) cos^2 x+ sin^2x= 1.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. Let (x, y) be a point on the terminal side of θ and let r be the distance from (0,0) to (x,y). If y = sin−1 x, then sin y = x,−π/2 ≤ y ≤ π/2.
(a) A node occurs at x = 0.15 m (b) An antinode occurs at x = 0.3 m (c) The speed wave is 5 ms –1 (d) The wavelength is 0.3 m. Inverses of trigonometric functions y sin 1 x if π 2 y π2 and sin y x y cos 1 x from MATH 1013 at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. Further, cos x = 0, if x = ±π/2, ±3π/2, ±5π/2.
Cos θ = sin (π/2 – θ) sin θ = cos (π/2 – θ) We’ve seen this before, but now we have it for any angle θ. Filling out the other trigonometric functions then gives cos(pi/2) = 0 (1) cot(pi/2) = 0 (2) csc(pi/2) = 1 (3) sec(pi/2) = infty (4) sin(pi/2) = 1 (5) tan(pi/2) = infty. Now, we will use the above concept for finding the values of sum and difference of angle of sin.
Let θ be an angle in standard position with vertex at (0,0). PHY003A – – Assignment 2 – solutions 2 π sin x a a a a 2 a 2 a 2 π π x x dx x sin 2 x dx xdx. When n=2 Cos(4+1)π/2= cos5π/2= cos450° = Cos(360+90)°=cos90°=0 When n=-1 Cos(-2+1)/π/2 = cos(-π/2) = cos(-90°) =Cos(90°) = 0 Hence cos(2n+1)π/.
7a – Proof of the law of cosines for acute angle γ by "cutting and pasting". As you can see, the result is a power series. I = e i π /2.
View PHY3A__Assignment2_solutions.pdf from PHY 003A at University of Johannesburg. To gain some confidence that this series really works as advertised, note that the substitution x = 0 provides the correct equation cos 0 = 1.Furthermore, substituting x = 1 into the first four terms gives you the following approximation:. The identities are extremely useful when dealing with sums of trigonometric functions, as they often allow for use of the.
π, 2π, 3π, then sin remains sin cos remains sin 2.The sign depends on the quadrant angle is in. Fundamentally, they are the trig reciprocal identities of following trigonometric functions Sin Cos Tan These trig identities are utilized in circumstances when the area of the domain area should be limited. Sin (π/2 – x) Since it is π/2, sin will become cos Here x is an acute angle So, π/2 – x = 90 – x is an.
May 16, 11 254 CHAPTER 13 CALCULUS OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS (LT CHAPTER 14) Use a computer algebra system to plot the projections onto the xy- and xz-planes of the curve r(t) = t cost,tsin t,t in Exercise 17. Notice that strictly speaking, the following definitions only define the trigonometric functions for angles in this range. There are many interesting applications of Trigonometry that one can try out in their day-to-day lives.
We can also state that if, for a given angle t, cos t = 5 13, t, cos t = 5 13, then sin (π 2 − t) = 5 13 sin (π 2 − t) = 5 13 as well. Cofunction Identities The cofunction identities in radians are listed in Table 1. Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond.
Find the linearization L(x) of the function at a = 5π/2. Now, we are aware of the expanded form of sum and difference of angle of cos. Here’s how you write it by using sigma notation:.
Note that the three identities above all involve squaring and the number 1.You can see the Pythagorean-Thereom relationship clearly if you consider the unit circle, where the angle is t, the "opposite" side is sin(t) = y, the "adjacent" side is cos(t) = x, and the hypotenuse is 1. Cos(90°= π /2) = `\color{blue}{\frac{1}{2} \sqrt{2 - \sqrt{2 + 2}} = 0}` sin(0°) Proofs 30° 45° and 60° Here are two simple triangles which give us the formulae for the trig values of these three angles:- This triangle is just a square cut along a diagonal. The inverse trigonometric identities or functions are additionally known as arcus functions or identities.
Free integral calculator - solve indefinite, definite and multiple integrals with all the steps. Y x z FIGURE 12 19. Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph.
Answer to Find the average value gave of the function g on the given interval. Which of the following is correct?. If γ is obtuse, and so cos γ is negative, then −ab cos γ is the area of the parallelogram with sides a and b forming an angle of γ′ = γ − π / 2.
When the cosine of y is equal to x:. (a) x(t) = cos(t) (b) x(t) = cos(t + π) (c) x(t) = cos(t/2) (d) x(t) = cos(7πt/2 + π/2) (e) x(t) = cos(t) + cos(2t) (f) x(t) = cos(t) + cos(2t) + cos(3t). Ex 3.3, 6 Prove that:.
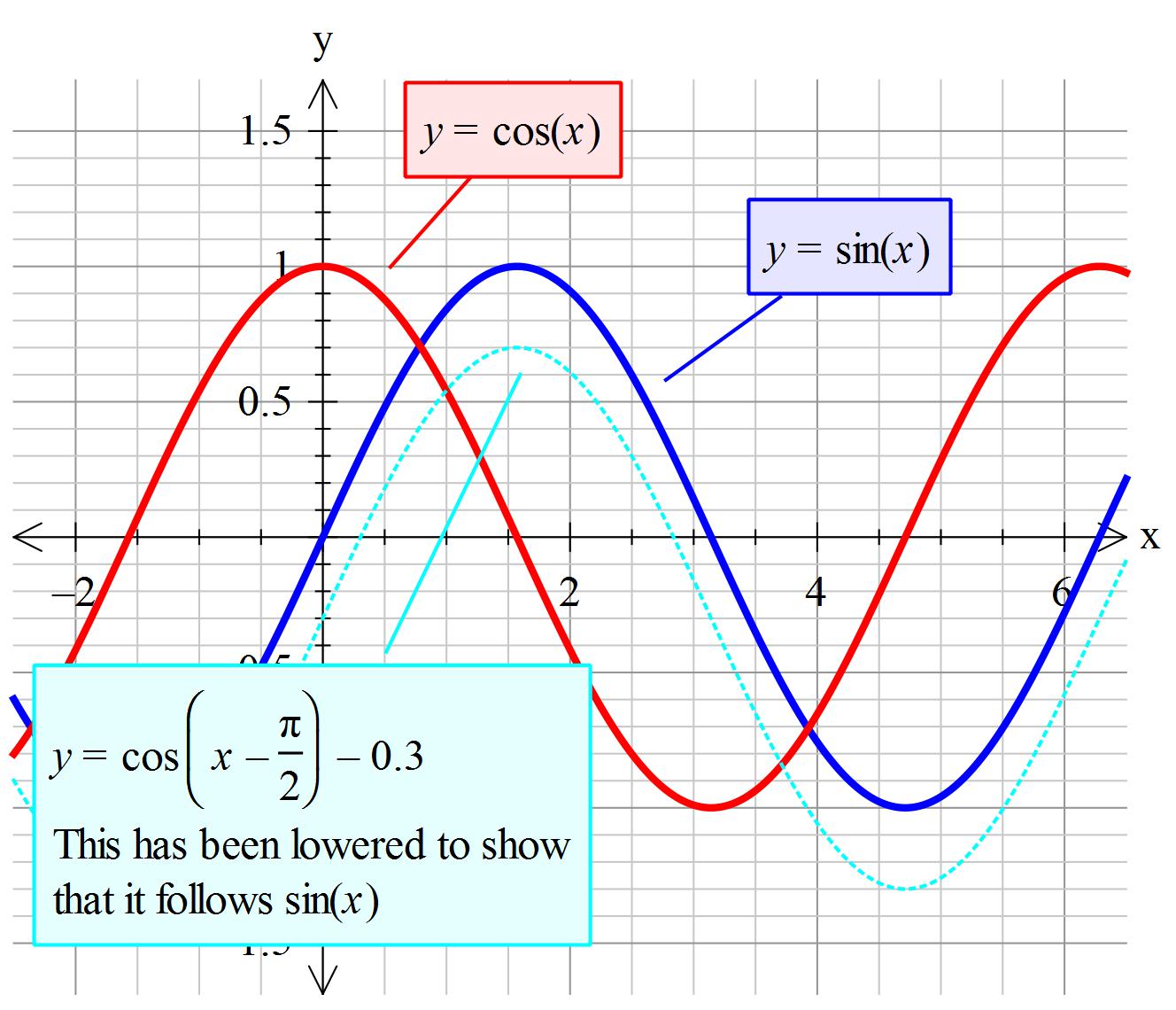
角度の単位としては原則としてラジアン (rad, 通常単位は省略) を用いるが、度 (°) を用いる場合もある。. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with step-by-step explanations, just like a math tutor. The sine and cosine graphs are almost identical, except the cosine curve starts at `y=1` when `t=0` (whereas the sine curve starts at `y=0`).
Therefore, to find y = sin−1(−3/22, we must find an angle y whose sine is -3/2. There are many possible angles with this sine, but the range of y = sin−1 x is restricted to , and so y must be in this interval. A wave disturbance in a medium is described by y(x, t) = 0.02 cos(50πt + π/2)cos (10πx) where x and y are in metre and t is in second.
R4 = 3 cos π 8 + cos π 4 + cos 3π 8 + cos π 2) π 8. While right-angled triangle definitions allows for the definition of the trigonometric functions for angles between 0 and radian (90°), the unit circle definitions allow. The identity is easily proved by forming a rectangle using two identical right triangles.
It’s true because when you reflect the plane across the diagonal line y = x, an angle is exchanged for its complement. Therefore, for a right triangle, the two non-right angles are between zero and π/2 radians. Therefore the general solution is.
All triangles are taken to exist in Euclidean geometry, so that the inside angles of each triangle sum to π radians (or 180°);. Arccos x = cos-1 x = y (Here cos-1 x means the inverse cosine and does not mean cosine to the power of -1). If θ θ is not in this domain, then we need to find another angle that has the same cosine as θ θ and does belong to the restricted domain;.
We have additional identities related to the functional status of the trig ratios:. So sin x = {1-cos^2 x)}^1/2 as cos x =2/3. π/2, 3π/2, 5π/2, then sin becomes cos cos becomes sin If the angle is multiple of π, i.e.
Cos(2n+1)π/2 is always zero when n€I For eg:- When n=1 Cos(2+1)π/2= cos3π/2 = cos270° which equals to 0. If cos x = 0, then consider cos-1 (0)= π/2. We get, Sin (π/2-x) = cos x.
That is express the number as r e i θ = r(cos(θ) + i sin(θ)) where θ is expressed in radians. Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationship between the sides and angles of a triangle. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
The curves align when. Cos (π/4−𝑥) cos (π/4−𝑦) – sin (π/4−𝑥) sin (π/4−𝑦) = sin(𝑥 + 𝑦) Taking L.H.S We know that cos (A + B) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B The equation given in Question is of this form Where A = (𝜋/4 −𝑥) B = (𝜋/4 −𝑦) Hence cos (π/4−𝑥) cos (π/4−𝑦) – sin (π. Cos(x - π/2) = sin x Example 3 Find the exact value of sin(15°) Solution to Example 3 15 ° is not a special angle.
この記事内で、角は原則として α, β, γ, θ といったギリシャ文字か、 x を使用する。. I i = (e i π /2) i = e i 2 π /2 = e-π /2. If the sides are of length 1, the diagonal is length √2.
If the angle is multiple of π/2, i.e. Sine and cosine are complementary:. Cos(u v) = cosucosv sinusinv tan(u v) = tanu tanv 1 tanutanv Double Angle Formulas sin(2u) = 2sinucosu cos(2u) = cos2 u sin2 u = 2cos2 u 1 = 1 22sin u tan(2u) = 2tanu 1 tan2 u Power-Reducing/Half Angle For-mulas sin2 u= 1 cos(2u) 2 cos2 u= 1+cos(2u) 2 tan2 u= 1 cos(2u) 1+cos(2u) Sum-to-Product Formulas sinu+sinv= 2sin u+v 2 cos u v 2 sinu sinv.
From the above discussion we can hence conclude that sin x = 0 when x = nπ, and cos x = o when x = (2n+1)π/2, where n is an integer. Simplify cos(x - π/2) Solution to Example 2 Use the difference formula (formula 2 above) for cosine to expand the given expression cos(x - π/2) = cos x cos π/2 + sin x sin π/2 cos π/2 = 0 and sin π/2 = 1, hence. This allows for easier analysis in many cases, as a single instance of a basic trigonometric function is often easier to work with than multiple are.
Then the arccosine of x is equal to the inverse cosine function of x, which is equal to y:. Hence a solution is x = ±π/2 + 2kπ If 2cos x – 1 = 0, this equation is equivalent to Now Hence a solution is x = ± π/3 + 2kπ. Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly.
Sin(x +y) can be written as cos π/2 –(x + y) which is equivalent. As, sin (π/2 – x) = cos (π/2 – (π/2-x) (by using identity 3). Then the arccosine of x is equal to the inverse cosine function of x, which is equal to y:.
Learn how to evaluate the limit of the quotient of cosx by π/2-x as the input x approaches π/2 in calculus. 1周 = 360度 = 2 π ラジアン. Sin(π/2 - X) = cosX cos(π/2 - X) = sinX tan(π/2 - X) = cotX cot(π/2 - X) = tanX sec(π/2 - X) = cscX csc(π/2 - X) = secX Addition Formulas cos(X + Y) = cosX cosY - sinX sinY cos(X - Y) = cosX cosY + sinX sinY sin(X + Y) = sinX cosY + cosX sinY sin(X - Y) = sinX cosY - cosX sinY tan(X + Y) = tanX + tanY / 1 - tanX tanY.
We say the cosine curve is a sine curve which is shifted to the left by `π/2\ (= 1.57 = 90^@)`. In cos x the value between 0 and pi/2 it is positive as is the value 3pi/2 & 2pi !!. Arccos 1 = cos-1 1 = 0 rad = 0° Graph of arccos.
For example, if you are on the terrace of a tall building of known height and you see a post box on the other side of the road, you can easily. For math, science, nutrition, history.
Solve For X Cos 1 X Sin 1 X 2 P 6 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sinx Youtube

Reciprocal And Quotient Identities Reference Acute Angle The Cast Rule Negative Angle Identities Cofunction Identities Reduction Formulas Periodicity Identities 9 Sideway Output To
Cos 2 のギャラリー
Prove That Sin 1 X Cos 1 X P 2 If X 1 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Graph Of Y Cos 2 X Pi 2 Mathtestpreparation Com

Cos P 11 Cos2p 11 Cos3p 11 Cos4p 11 Cos5p 11 1 32 Brainly In
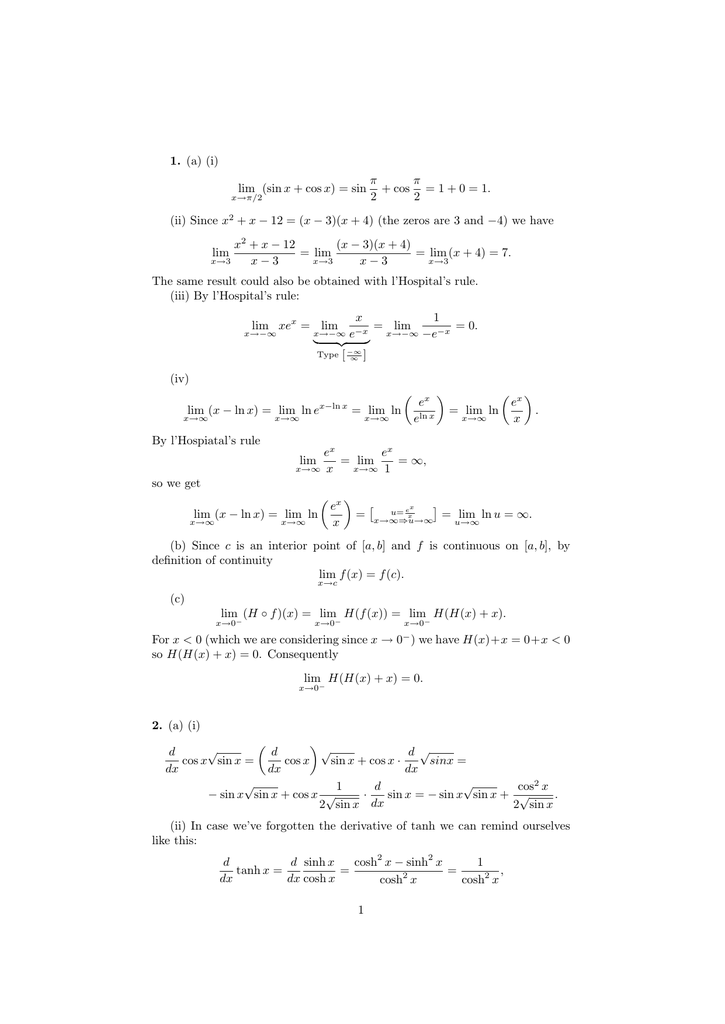
1 A I Lim Sin X Cos X Sin P 2 Cos P 2 1 0 1 Ii Since X2

The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl

Example 15 Prove Cos Pi 4 X Cos Pi 4 X Root 2 Cos X
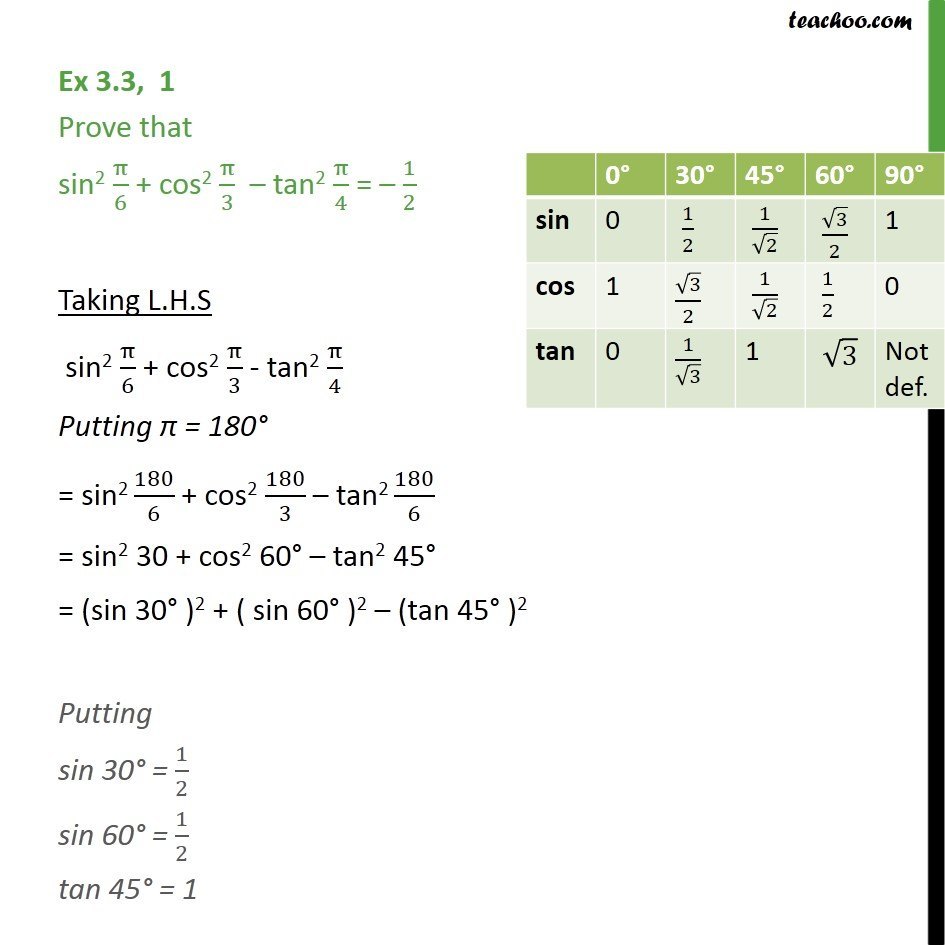
Ex 3 3 1 Prove Sin2 Pi 6 Cos2 Pi 3 Tan2 Pi 4 1 2
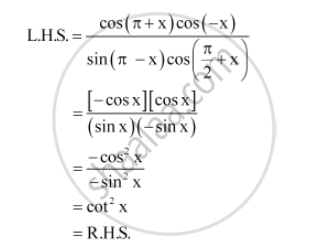
Prove That Cos Pi X Cos X Sin Pi X Cos Pi 2 X Cotsqrt2 X Mathematics Shaalaa Com
Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions
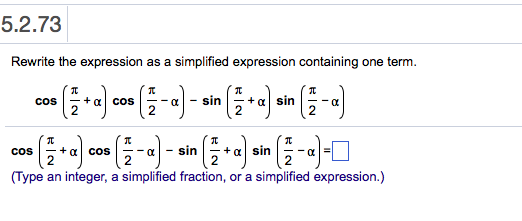
Solved Rewrite The Expression As A Simplified Expression Chegg Com
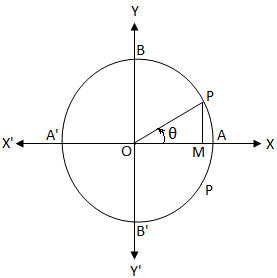
Cos Theta Equals 0 General Solution Of The Equation Cos 8 0 Cos 8 0

Cos Pi 2 Does Not Equal 0 Why Ptc Community
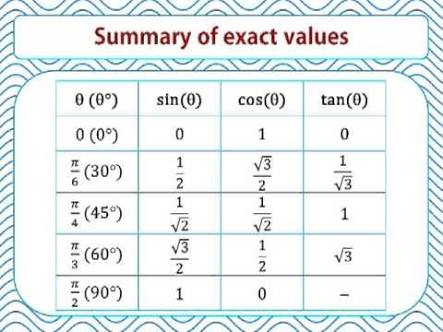
How Do You Find The Value Of Cos Pi 4 Socratic
Unit 3 5 1 Bingo Card

The Expression Tan X Pi 2 Cos 3pi 2 X Sin 37pi 2 X Cos X Pi 2 Tan 3pi 2 X Simplifies To 1 Cos2x Sin2x Math Trigonometric Functions 1040 Meritnation Com
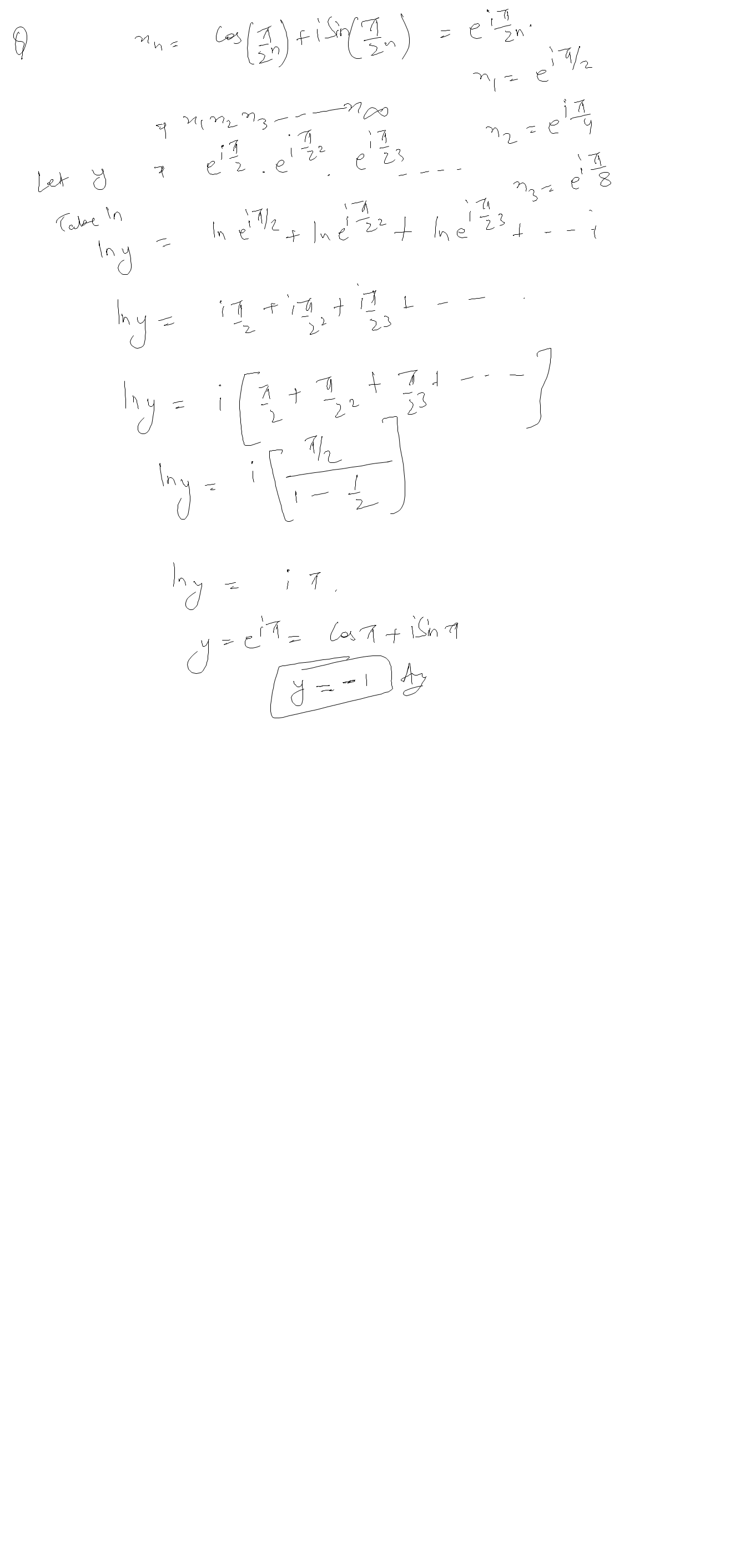
X N Cos P 2 N I Sin P 2 N N Is An Element Of N Then X 1 X Askiitians

Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle
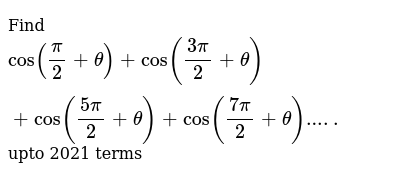
Find Cos Pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta Cos 5pi 2 Theta C

Prove Csc Pi 2 X Sec X Brainly Com

If X R Cos Pi 2 R I Sin Pi 2 R Z T Cos Pi 3 T I Sin Pi 3 T Where R 1 2 Youtube
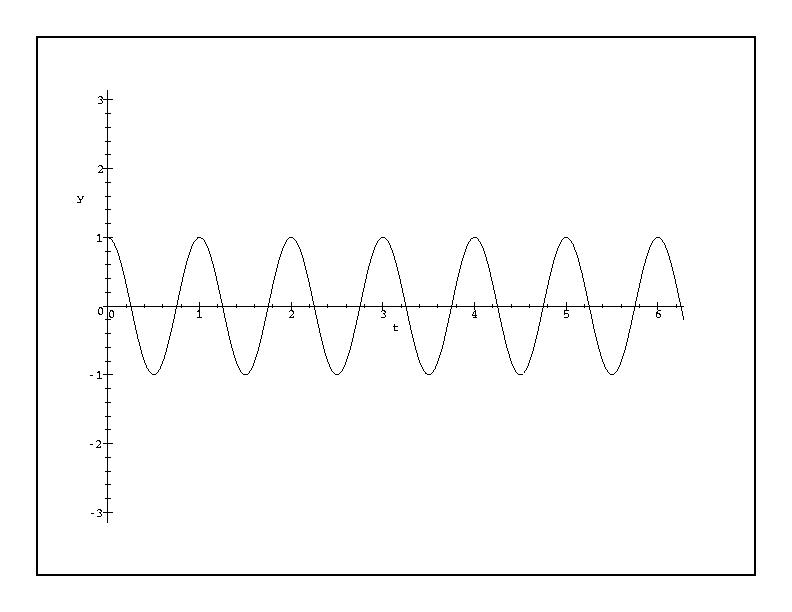
Plot Of Cos 2 Pi T
What Is The Exact Value Of Cot Pi 2 Socratic

Which Are Anti Derivatives Of F X Sin X Cos X 1 All Of Them 2 F 1 Only 3 None Course Hero
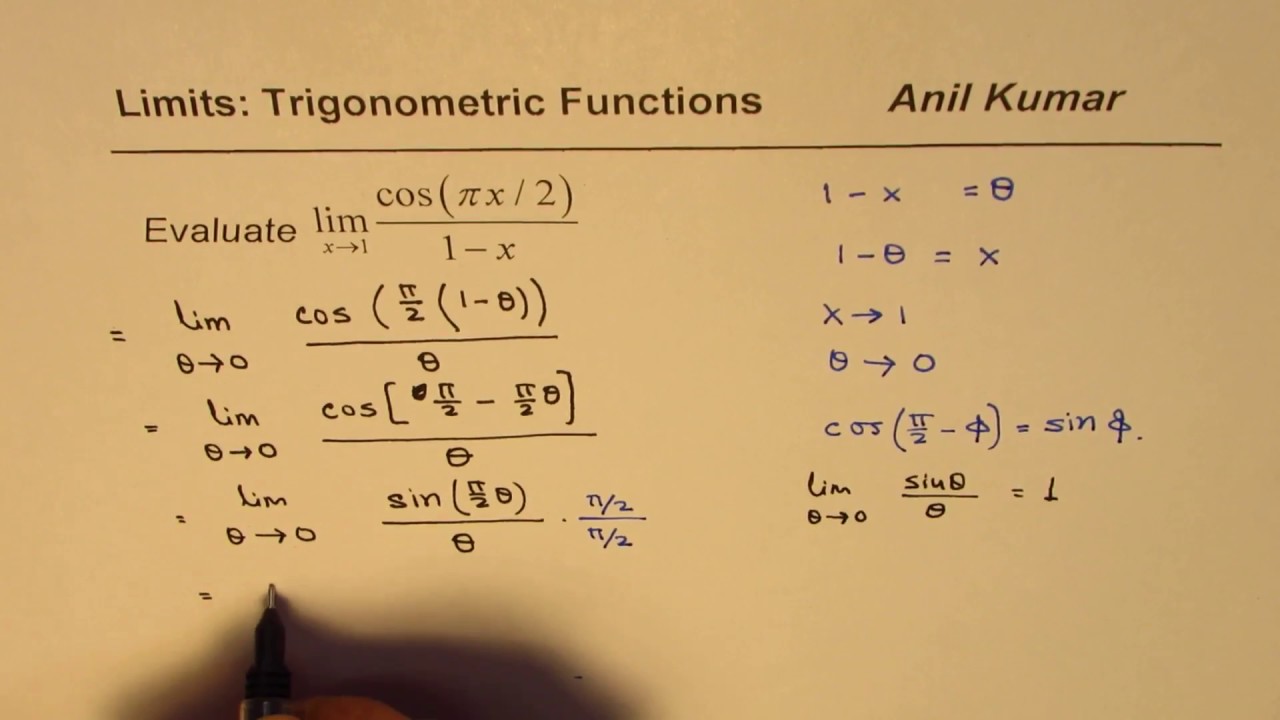
Limit Trigonometric Function Cos Pi X 2 1 X By Substitution Youtube

Express Tan 1 Cosx1 Sinx P2 X P2 In The Simplest Form
How To Prove Math Cos Pi 9 Cos 2 Pi 9 Cos 4 Pi 9 1 8 Math Quora
3 Graphs Of Y Asin Bx C And Y Acos Bx C

Solved Evaluate The Indefinite Integral Int Cos Pi X 2 Chegg Com
Answer Key Chapter 8 Algebra And Trigonometry Openstax

Proving Left Frac 1 Sin X I Cos X 1 Sin X I Cos X Right N Cos N Left Frac Pi 2 X Right I Sin N Left Frac Pi 2 X Right Mathematics Stack Exchange

Prove That I Cos P 3 X 1 2 Cosx 3sinx Edurev Class 11 Question
Modeling With Trigonometric Equations Precalculus Ii

Example 29 Prove Cos2 X Cos2 X Pi 3 Cos2 X Pi 3

Trigonometry Angles Pi 2 From Wolfram Mathworld
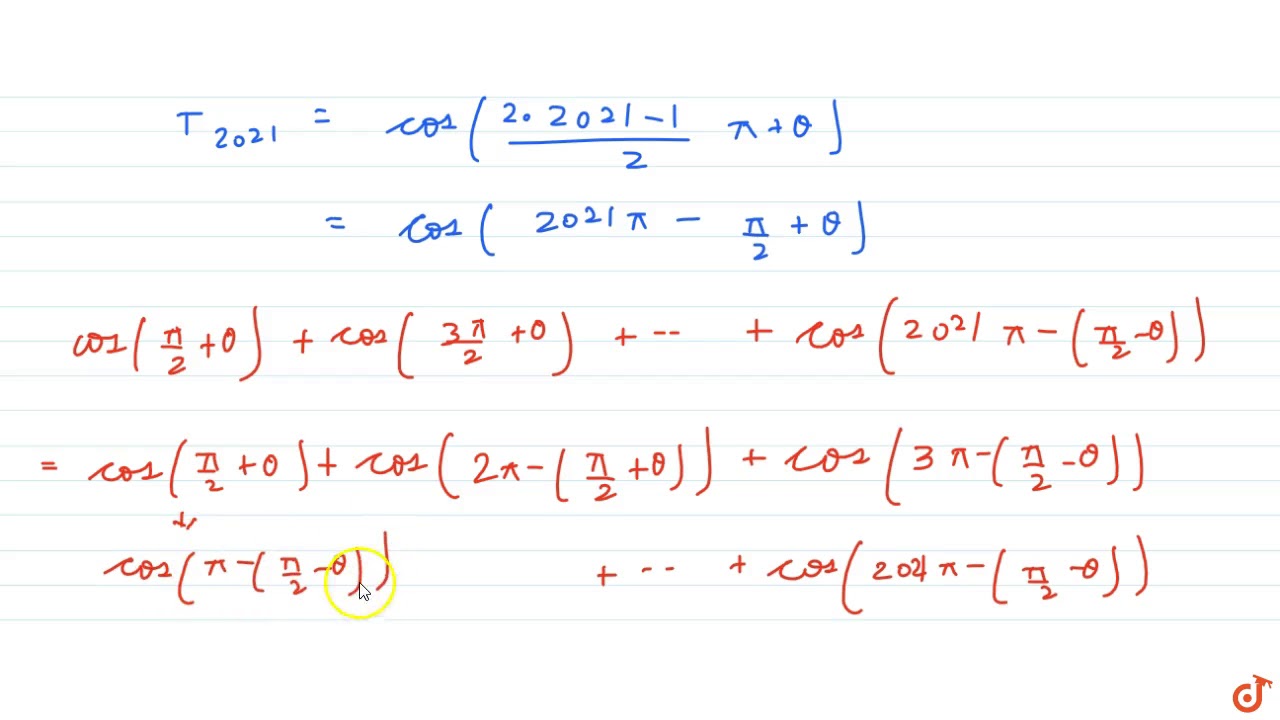
Find Cos Pi 2 Theta Cos 3pi 2 Theta Cos 5pi 2 Theta Cos 7pi 2 Theta Upto Youtube
Barnett Ziegler Byleen Chapter 4 Ppt Video Online Download
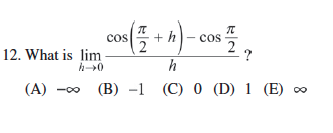
Solved What Is Lim H Rightarrow 0 Cos Pi 2 H Cos Pi Chegg Com
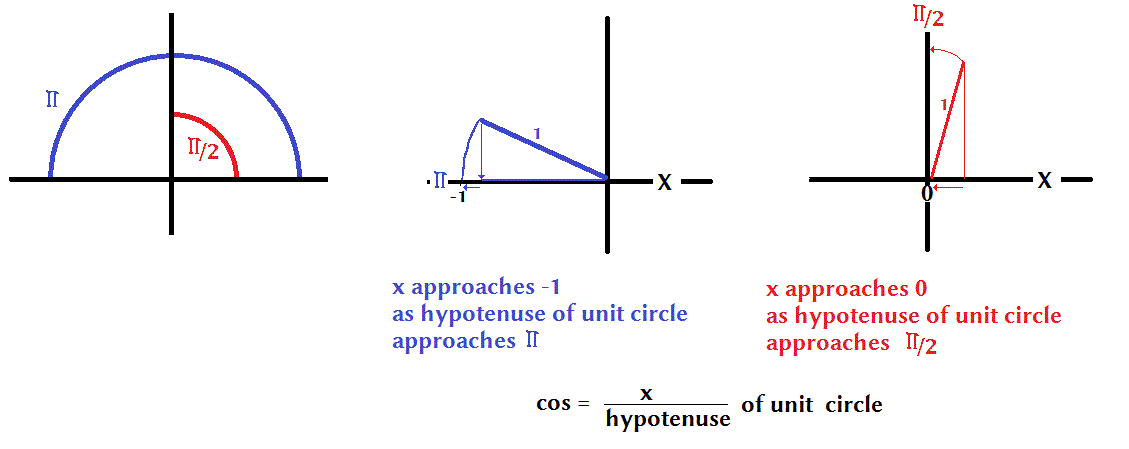
How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos Pi 2 Socratic

Wallis Product Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsfkihu Hlprxqlhaw2q5mg8z P1telz7etrxmgc3d4 Dpezwcn Usqp Cau

Trigonometric Functions Introduction Sine Cosine Videos And Examples
How Do You Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sin X Socratic
Q Tbn 3aand9gcru2e6rhyd3hj1lqqfuidb8kf9jhvqbyeawxwlrr O Usqp Cau
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqp2ewonuqfca 6kuhio2ythbag7rhmwfkbpdwv3n3whxbrxkrc Usqp Cau

The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl

A State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval 3pi 2 2pi B State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval Pi 2 Pi Study Com

Trigonometric Function Errors At Pi Or Pi 2 Such As Sin Pi Or Cos Pi 2 File Exchange Matlab Central
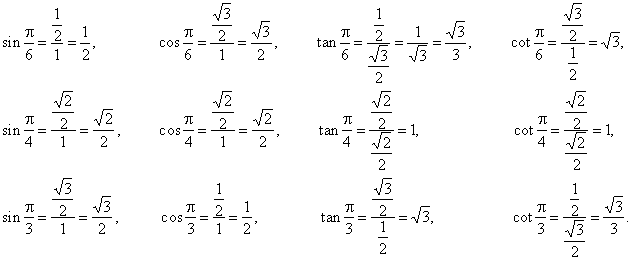
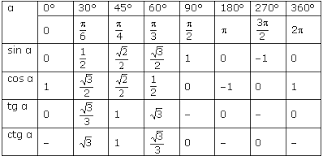
Values Of Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs Pi 6 Pi 4 And P 3 The Values Of The Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs That Are Multipliers Of 30 Degrees Pi 6 And 45 Degrees Pi 4

Algebra Trig Review

Solved Find The Exact Trig Value For Each Expression Sin Chegg Com

Trigonometric Identity Review Trigonometry Identities Reciprocal Identities Sin 8 Cos 8 Tan 8 Quotient Identities Tan 8 Cot 8 Ppt Download

A Simple Harmonic Motion Is Represented By Y 5 Sin 3 P T 3 Cos 3 P T Cm The Amplitude And Time Period Of The Motion Are

How To Solve Cos Pi 2 T Ge 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
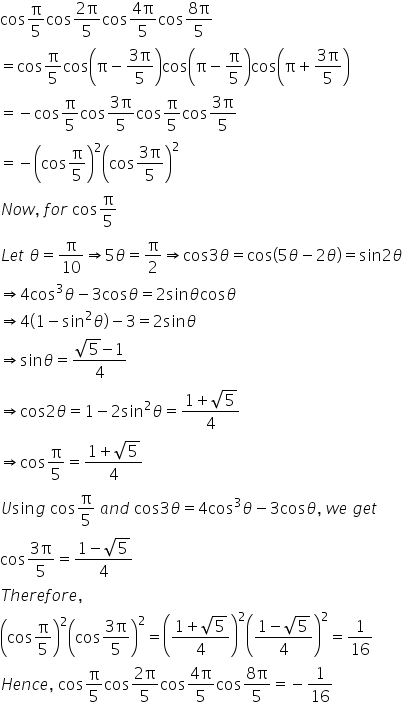
To Prove Cos Pi 5 Cos 2 Pi 5 Cos 4 Pi 5 Cos 8 Pi 5 1 16 Please Answer Soon Mathematics Topperlearning Com Jhw7xbb
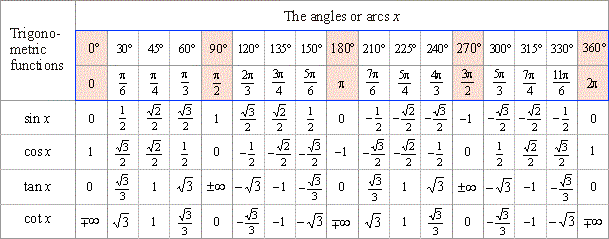
Values Of Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs Pi 6 Pi 4 And P 3 The Values Of The Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs That Are Multipliers Of 30 Degrees Pi 6 And 45 Degrees Pi 4

Biomath Trigonometric Functions
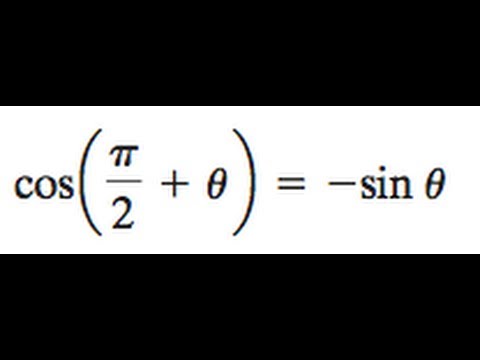
Prove Cos Pi 2 Theta Sin Theta Youtube

The Taylor Series For F X Cos X At A Pi 2 Is S Chegg Com Taylor Series Homework Help Math

Graph Sine And Cosine Functions

The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl

What Is Cos Pi 2 H Cos Pi 2 H A H Approaches 0 Youtube

Prove That Cos 2 Pi 12 Cos 2 Pi 4 Cos 2 5pi 12 3 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Imee8mvv
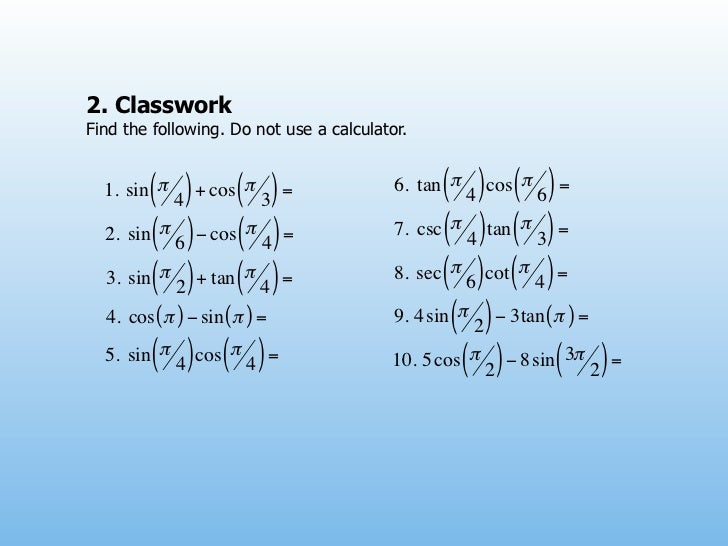
Week 10 Trigonometry

2 Assume 0 8 P 2 So That Sin 8 0 And Cos 8 0 If X Y Is Download Scientific Diagram

Inverse Trigonometric Functions Precalculus Ii
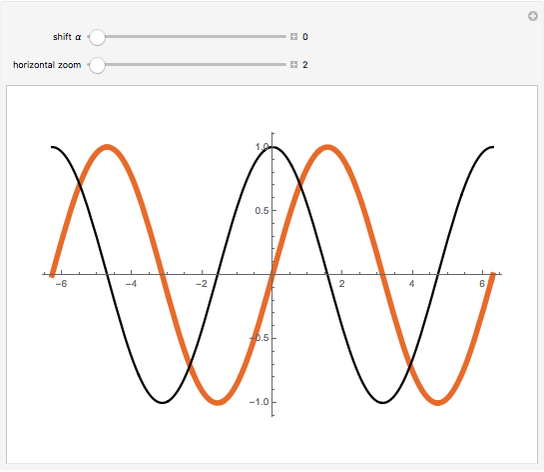
Sin T Cos Pi 2 T Wolfram Demonstrations Project
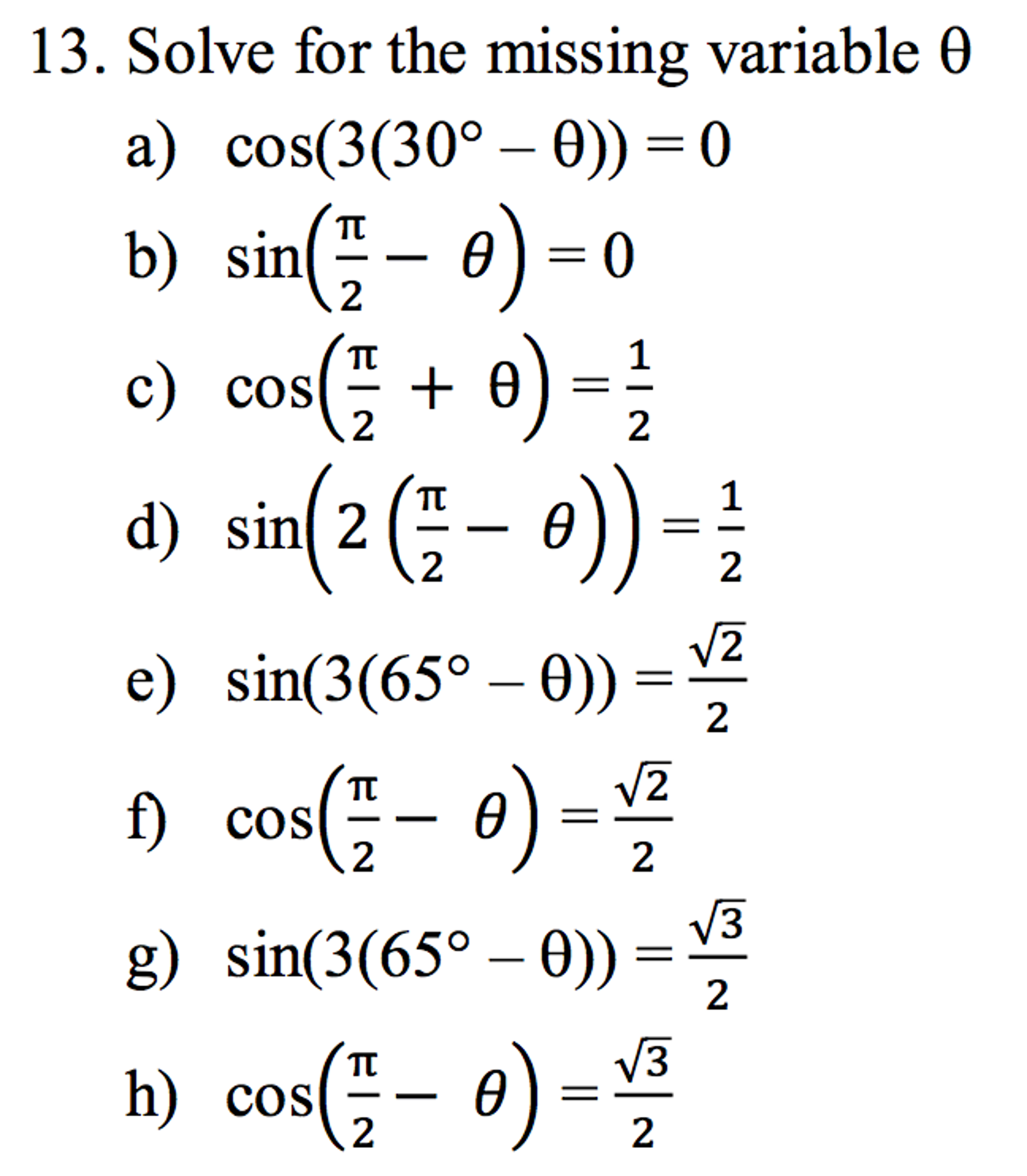
Solved Solve For The Missing Variable Theta Cos 3 30 Degr Chegg Com
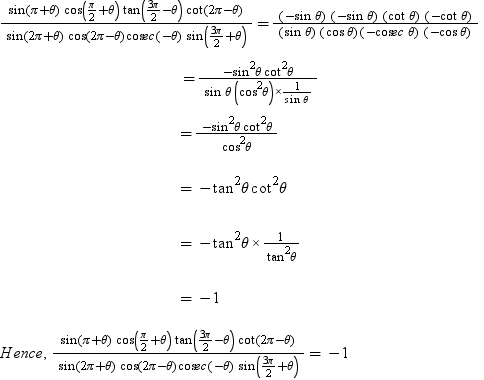
Evaluate Sin Pi Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Tan 3pi 2 Theta Cot 2pi Theta Sin 2pi Theta Cos 2pi Theta Cosec Theta Sin 3pi 2 Theta Math Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com

The Taylor Series For F X Cos X At A Pi 2 Is S Chegg Com Taylor Series Polynomials University Tips

The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl

Cos Pi 2n 1 Cos 3pi 2n 1 Upto N Terms Equals

Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia

List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia

1 3 Trigonometric Functions

Answered Find Cos 8 And Tan 8 If Sin 8 0 4 And Bartleby

Alpha Computational Knowledge Engine Sins Mathematics Knowledge
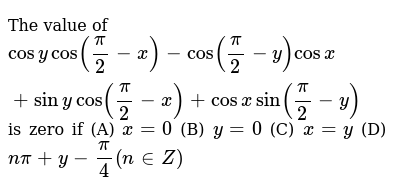
The Value Of Cosycos Pi 2 X Cos Pi 2 Y Cosx Sinycos Pi 2 X Cosx

Frac 1 4rs R S 2 Cos Frac Pi 2 R S S R 2 Cos Frac Pi 2 S R Near 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Graph Of Cosine Function Mathtestpreparation Com

Cosine Function

Trigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bank
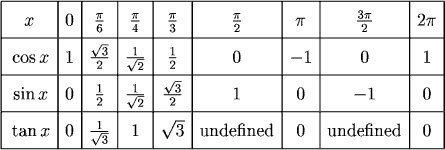
Um Math Prep S14 2 Function Values
Math Tutor Functions Theory Elementary Functions

Sci Science Math

Why Is Mathematica Converting Sin X Pi 2 To Cos X Mathematica Stack Exchange
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrke K36wh6xkf2egm3xcjx80bjs V Ldzxr4b8yvatalqjq4zu Usqp Cau
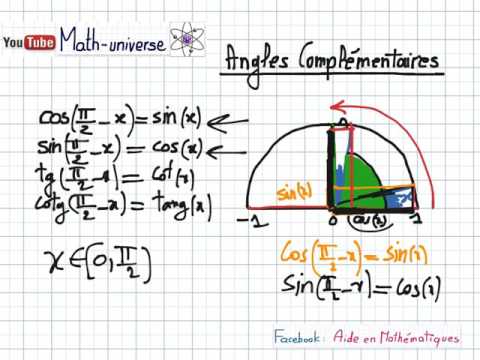
Trigonometrie Partie 4 Cos P X Cos P 2 X 2eme Annee Sc Info Youtube

What Is The Value Of Sin N Pi 2 Quora
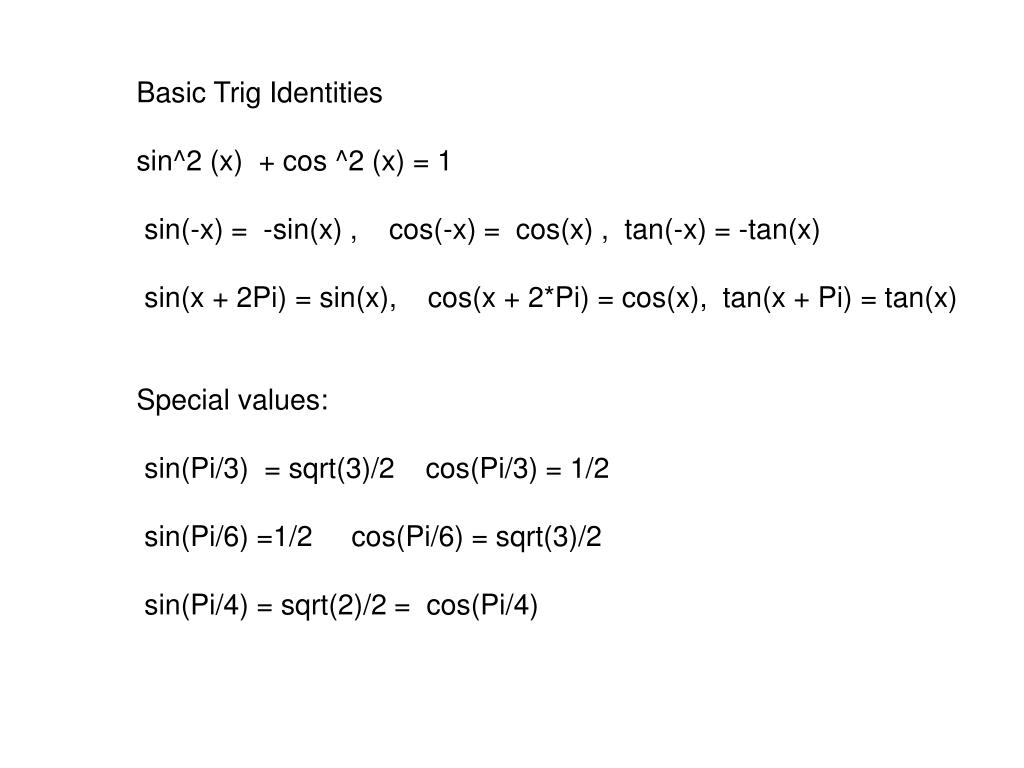
Ppt Basic Trig Identities Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 Powerpoint Presentation Id
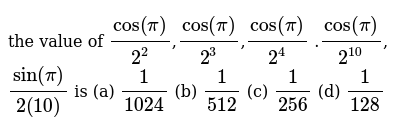
The Value Of Cos Pi 2 2 Cos Pi 2 3 Cos Pi 2 4

Trigonometry Trigonometric Analysis Wikiversity
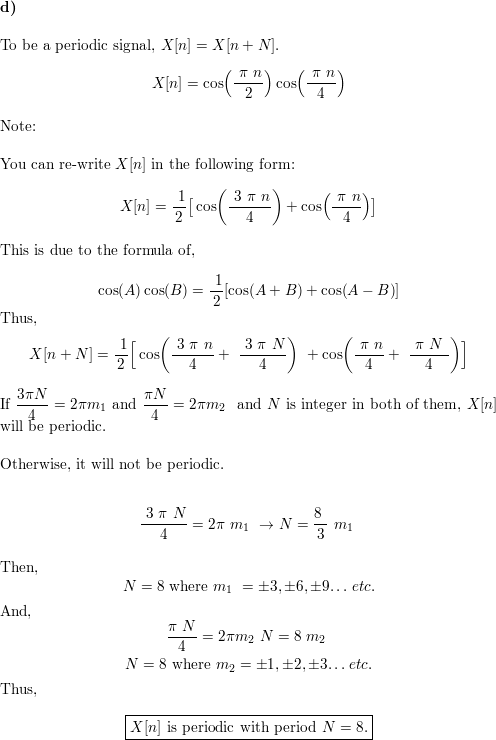
Determine Whether Or Not Each Of The Following Discrete Time Signals Is Periodic If The Signal Is Periodic Determine Its Fundamental Period A X N Sin 8p 2 N 1 B X N Cos R 8 P C X N Cos P 8 N D X N Cos P 2 N

Proof Of The Reduction Formulas For Angles 90 A Or P 2 A Mathvox

Prove That Cos P X Cos X Sin P X Cos P

Lesson The Amazing Unit Circle Trigonometric Identities
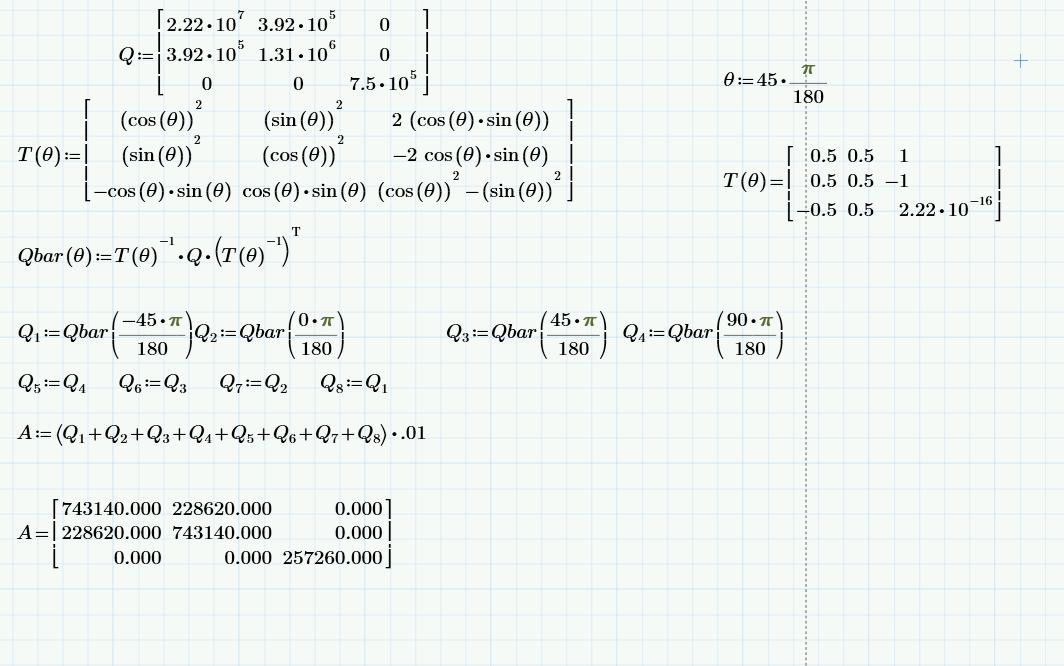
Cos Pi 2 Does Not Equal 0 Why Ptc Community
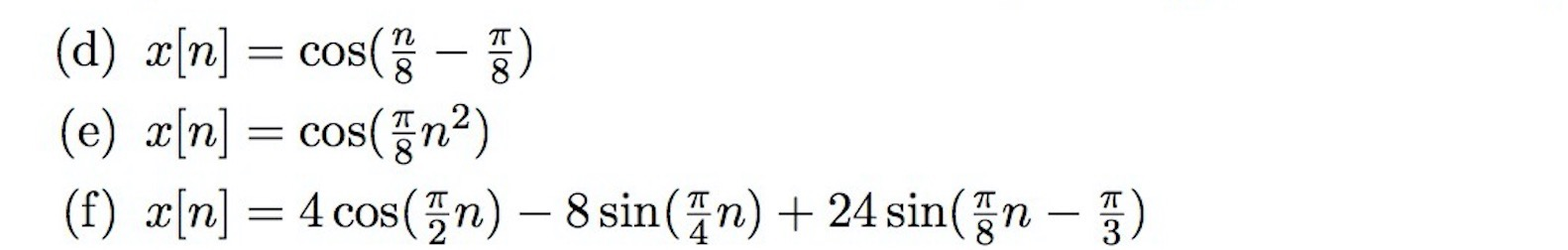
Solved D X N Cos N 8 Pi 8 E X N Cos Pi 8 N 2 Chegg Com
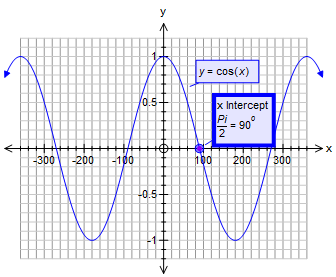
How Do You Find The Value Of Cos Pi 2 Using The Graph Socratic
How To Simply Prove That Cos P 2 X Sinx Quora
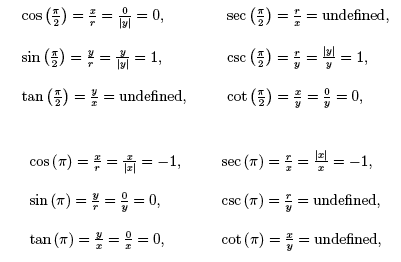
Biomath Trigonometric Functions
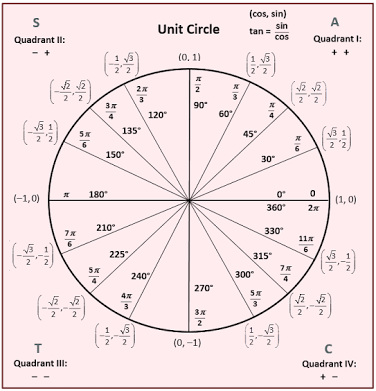
Using The Unit Circle How Do You Find The Value Of The Trigonometric Function Sec Pi 2 Socratic



